what is ketoacidosis diabetic Ketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications ketosis keytones live fever risks sugar
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a condition that affects individuals with diabetes. It occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are acidic chemicals formed when the body breaks down fat for energy in the absence of sufficient insulin. DKA can be a serious and life-threatening condition if left untreated, so it is important to recognize the symptoms and seek prompt medical treatment.
Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
One of the key symptoms of DKA is frequent urination. The excess ketones in the body cause increased thirst and urination as the body tries to eliminate them. You may also experience extreme fatigue and weakness, as the lack of insulin prevents the cells from getting the glucose they need for energy.
Another common symptom is vomiting and nausea. DKA can cause your stomach to empty more slowly, leading to feelings of fullness, bloating, and indigestion. Additionally, because your body isn’t receiving enough glucose, your muscles may begin to break down, resulting in muscle aches and cramps.
DKA can also affect your mental state, causing confusion, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. This is because the high levels of ketones can disrupt normal brain function. Other symptoms to watch out for include fruity-smelling breath, rapid breathing, and flushed skin.
Treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
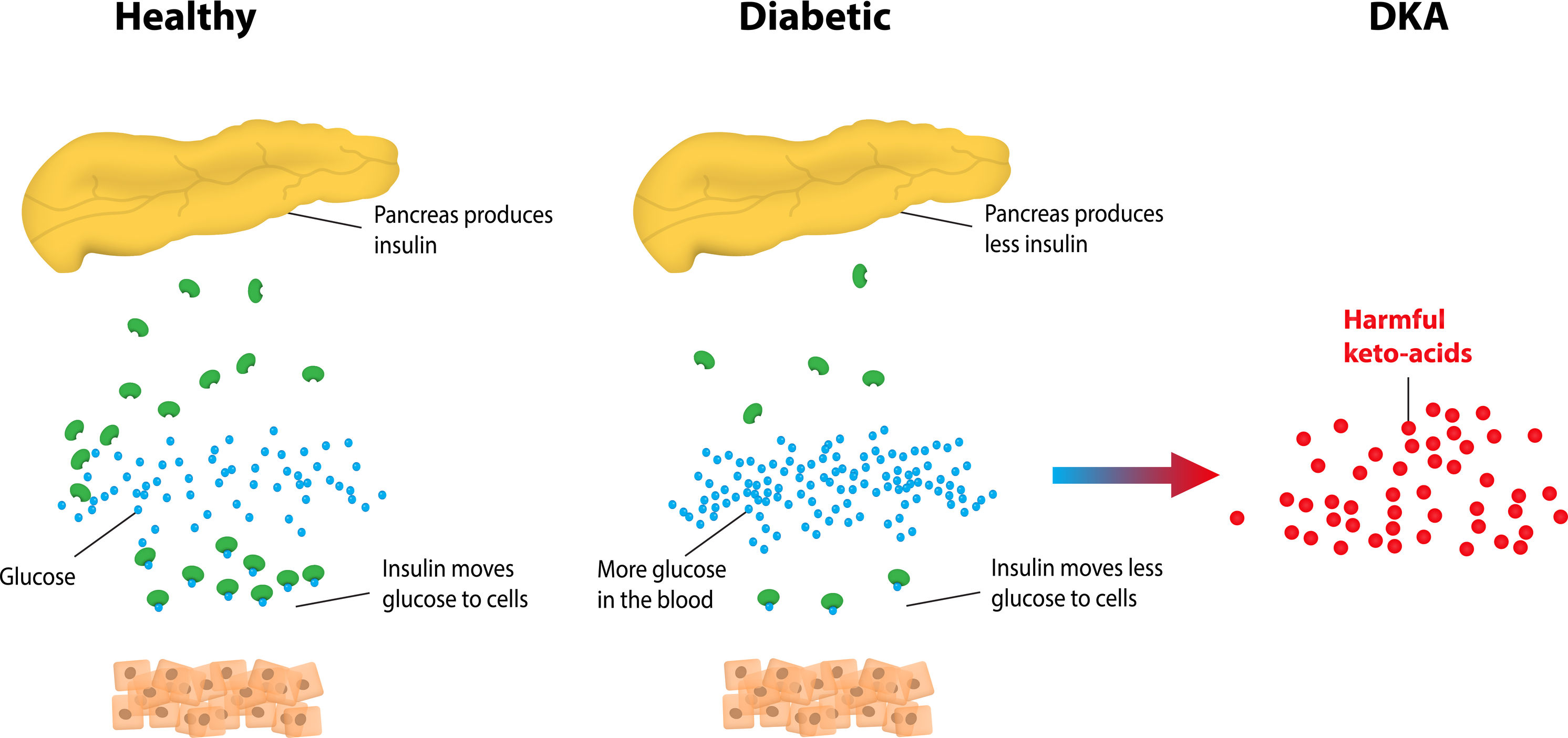 If you suspect that you or someone you know is experiencing DKA, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. DKA is a medical emergency and requires hospitalization for proper treatment.
If you suspect that you or someone you know is experiencing DKA, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. DKA is a medical emergency and requires hospitalization for proper treatment.
Typically, the treatment for DKA involves administering intravenous fluids to rehydrate the body, as well as insulin to lower blood sugar levels. In severe cases, electrolytes may also need to be replaced. It is crucial to closely monitor blood sugar levels and adjust insulin doses as necessary. Regular monitoring of other vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and urine output, is also important during treatment.
After initial treatment, it is important to address the underlying cause of DKA and take steps to prevent its recurrence. This may involve adjusting insulin doses, closely monitoring blood glucose levels, and making lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthier diet and engaging in regular physical activity.
It is important to remember that DKA can be a preventable complication of diabetes. By carefully managing your diabetes, monitoring your blood sugar levels, and seeking regular medical care, you can reduce the risk of developing DKA.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing the symptoms of DKA, do not hesitate to seek medical attention. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications and ensuring a healthy outcome.
If you are searching about What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition like Study: SGLT-2 Inhibitors Raise Risk of Diabetic Ketoacidosis – Diabetes, What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition and also Ketoacidosis. Read more:
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition
 www.allinallnews.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type ketosis treatment mechanism vs symptoms sepsis ketogenic nurse sugar signs notes cancer definition body
www.allinallnews.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type ketosis treatment mechanism vs symptoms sepsis ketogenic nurse sugar signs notes cancer definition body
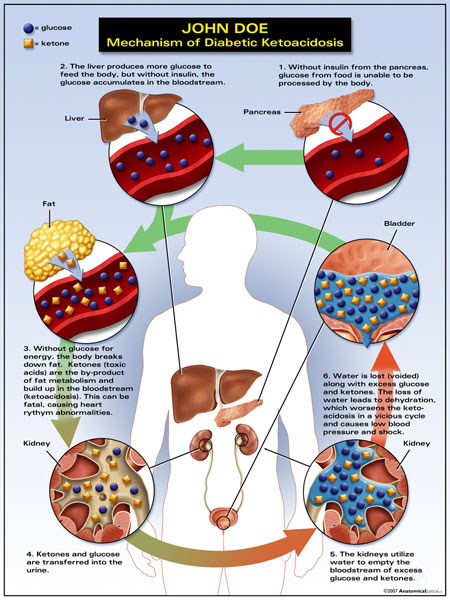
Pathogenesis Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.netketoacidosis diabetic pathogenesis diagram
www.researchgate.netketoacidosis diabetic pathogenesis diagram
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Ketosis Symptoms And Treatment | Diabetes UK
 www.diabetes.org.ukdka ketoacidosis diabetic complications symptome fruity ketosis ketones mellitus anzeichen mantracare abdominal ursachen urine coma occasionally affects
Study: SGLT-2 Inhibitors Raise Risk Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis – Diabetes
 www.diabetesdaily.comketoacidosis diabetic diabetes sglt raise inhibitors risk study
www.diabetesdaily.comketoacidosis diabetic diabetes sglt raise inhibitors risk study
Ketoacidosis
 diseasesandconditions.netketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications ketosis keytones live fever risks sugar
diseasesandconditions.netketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications ketosis keytones live fever risks sugar
Ketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications ketosis keytones live fever risks sugar. What is diabetic ketoacidosis (dka). Ketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes nursing type ketosis treatment mechanism vs symptoms sepsis ketogenic nurse sugar signs notes cancer definition body